Wall Street predicted a big surge for oil this year. But prices are
OPEC Secretary General Haitham Al Ghais said finger-pointing and misrepresenting the actions of OPEC and OPEC+ was “counterproductive.”
Anton Petrus | Moment | Getty Images
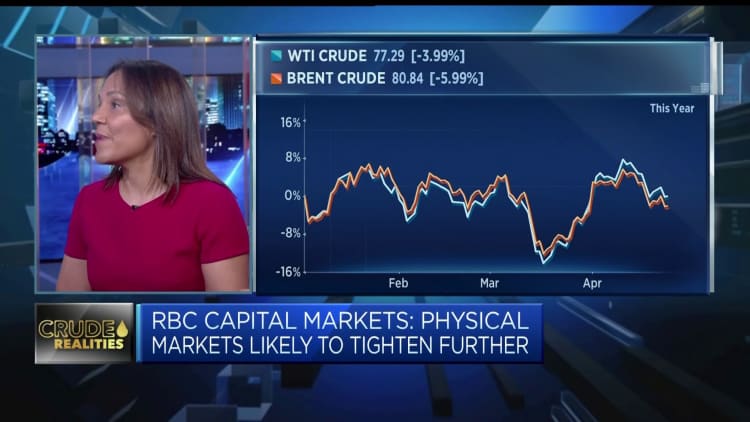
A surprise decision by several OPEC+ producers to voluntarily cut output earlier this month had pushed analyst oil price forecasts near $100 per barrel, but stagnating prices now point to a deepening divide between macroeconomic sentiment and supply-demand fundamentals.
Oil prices have once again lulled near the $80 per barrel threshold, nearly revisiting territory walked in early April, before members of the OPEC+ coalition announced a unilateral cut totaling 1.6 million barrels per day until the end of the year.
The production declines prompted some analysts to warn prices could surge to triple digits, with Goldman Sachs adjusting its Brent forecast up by $5 per barrel to $95 per barrel for December 2023.
Analysts now flag that broader financial turmoil has so far obstructed this bullish outlook, as supply-demand factors are outweighed by recessionary concerns.
“Oil markets have completely faded the boost from the surprise OPEC+ cut earlier this month, and we think this primarily reflects deep pessimism about the macro outlook, with little evidence of incremental weakness in demand so far,” Barclays analysts said in a Wednesday note.
“Weaker refining margins and freight demand have been in focus recently, but we believe markets might be reading too much into the implications of these trends for the demand outlook. We also think that markets might be underestimating OPEC+’s resolve to keep the inventory situation in check.”
“People really bet on a China reopening,” Helima Croft, managing director and global head of commodity strategy at RBC Capital Markets, told CNBC’s “Squawk Box” on Wednesday.
Beijing, the world’s largest importer of crude oil, reined in its purchases last year amid drastic “zero-Covid” restrictions that depressed transport fuel requirements. China has been progressively lifting its pandemic measures since the end of last year, and local crude oil demand is returning — but at a more “muted” pace, Croft noted.
“And the issue of the Fed is real. I think that is something that a lot of us got wrong in terms of the impact of, you know, the rate hikes, recession concerns,” she added.
“We have these OPEC cuts in place, we do have, you know, again, strong demand in India, China is reopening — this should be set up for a bullish story. People are still optimistic about the back half of the year, but the question is, can you get through the big macro wall of worry?”
Viktor Katona, lead crude analyst at Kpler, told CNBC by e-mail that oil prices have suffered from a “constant barrage of gloomy macroeconomic news that creates a negative sentiment background,” as well as market distrust in the implementation of the OPEC+ production cuts. Market participants often wait for a visible reflection — such as lower export rates — to factor in production cuts, which can…
Read More: Wall Street predicted a big surge for oil this year. But prices are
